Categories
- Case & News (50)
- Blog (580)
A set of complete concrete batch plant usually consists of core equipment, auxiliary systems and intelligent modules. Its design needs to take into account production efficiency, environmental protection requirements and intelligent management. It is a complex system engineering used to continuously and automatically produce fresh concrete that meets quality requirements. The specifications of concrete batching plants range from HZS25 (25 cubic meters/hour) to HZS240 (240 cubic meters/hour). The theoretical annual output of a 120 cubic meters/hour concrete batch plant can reach 288 tons/hour. For special scenes such as plateaus and oceans, the equipment needs to enhance thermal insulation and anti-corrosion performance. For example, the special concrete batch plant can operate stably at a temperature difference of -30℃ to 50℃ by optimizing the pipeline system.
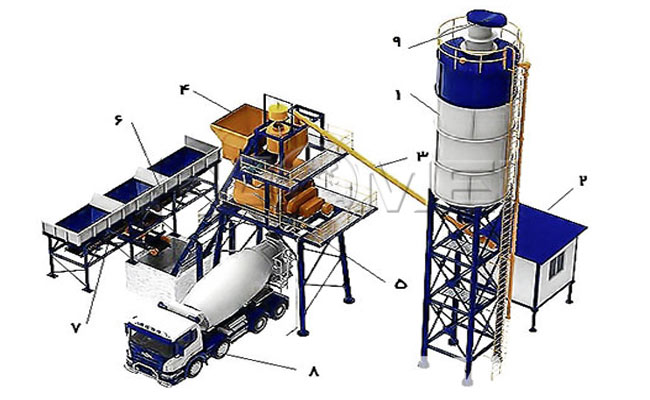
1. Core system and equipment
– Mixer host
As the core of the complete concrete batch plant, the mainstream adopts a twin-shaft forced concrete mixer (such as the JS series) to achieve uniform mixing of aggregates, cement, water and other materials through high-speed rotating blades. Large projects may be equipped with dual stations (such as 2HZS120), with production capacity increased to 240 cubic meters/hour. Some high-end models are equipped with stepless hydraulic systems, which reduce energy consumption by 15%.
– Batching and weighing system
Aggregate batching: The batching station with modular design can handle more than 3 materials at the same time, and the electronic scale can achieve accurate measurement of aggregates such as sand and gravel, with the error controlled within 2%.
Powder transportation: Powders such as cement and fly ash enter the metering hopper through a screw conveyor or pneumatic conveying system. The silo is equipped with a pressure safety valve, a level indicator and a bag dust collector to prevent dust leakage.
Liquid metering: Water and admixtures are controlled by independent metering pumps, and the slump is monitored in real time with AI visual technology, and the ratio is adjusted dynamically to ensure stable concrete performance.
– Conveying and storage system
Horizontal transportation: Belt conveyors are used for aggregate transportation, and trough belts can reduce space occupancy; screw conveyors are responsible for vertical transportation of powders and have strong sealing.
Vertical lifting: Use bucket elevator or lifting belt to send materials into the waiting silo above the mixing host.
Storage facilities: The aggregate silo adopts a semi-enclosed structure and is equipped with a fog cannon to reduce dust; the powder silo (such as prefabricated steel silo) can store up to 100-1000 tons and supports rapid disassembly and assembly.
– Control system
Intelligent control: The whole process is automated through PLC or computer system, supporting formula storage, data traceability and remote monitoring.
Human-computer interaction: The operation interface integrates real-time data monitoring, fault warning and production report generation functions. Some high-end systems can also optimize mixing parameters through AI algorithms.
2. Environmental protection and safety configuration
– Dust control
Organized emission: Bag dust collectors are installed on the top of the concrete mixer and cement silo, and the particle emission concentration is ≤10mg/m³, meeting the special limit of the “Emission Standards for Air Pollutants in Cement Industry”.
Unorganized emissions: The three sides of the aggregate yard are closed and covered with tarpaulins. The transport vehicles are closed tank trucks. The factory roads are regularly sprinkled with water to ensure that the dust concentration at the factory boundary is ≤0.5mg/m³.
– Wastewater treatment
The production wastewater is recycled after being treated in a multi-stage sedimentation tank, and the wastewater from the car wash station is recycled into aggregates through a sand and gravel separation system to achieve zero emissions. For example, the reclaimed water treatment system can increase the wastewater reuse rate to more than 95%.
– Noise control
Low-noise equipment (such as silent screw conveyors) is selected, and soundproof covers are installed for strong noise sources. The factory boundary noise is ≤60dB during the day and ≤50dB at night, which meets the standards of industrial enterprises.
– Safety management
Equipped with video surveillance, infrared detection of weighbridges and vehicle positioning systems throughout the factory area to track the transportation route and unloading status in real time to prevent material leakage or excessive transportation.
3. Intelligent and modular innovation
– Modular design
The complete concrete batch plant adopts a building block structure, and the core functional units (such as metering modules and mixing modules) can be quickly disassembled and assembled. For example, designed with modular design, and the installation period is shortened from 23 days to 12 days, and it supports transfer and reuse.
– Digital management
The concrete batch plant is connected to the intelligent management platform to realize the dataization of the entire process of raw material acceptance, mix ratio design, and transportation scheduling. Through electronic access control and intelligent material level monitoring, risks such as “wrong warehouse” can be avoided, and inventory errors can be corrected in real time.
In summary, a set of complete concrete batch plant is a highly automated production system: raw materials (sand, stone, cement, fly ash, water, admixtures) start from their respective storage locations -> measured according to precise formula -> transported to the mixing host -> fully mixed -> finished concrete is unloaded into the mixer truck -> transported to the construction site. Its design goal is to achieve high-efficiency, low-cost, environmentally friendly and clean continuous production under the premise of ensuring stable and reliable concrete quality.